Title:14012020-Mapping essential genes in WT and getting insights from it.
Contents
62. Title:14012020-Mapping essential genes in WT and getting insights from it.#
62.1. Date#
14012020
62.2. Objective#
To analyze and get some insights from the essential genes in WT. Useful questions:
How many essential genes in WT are also bem1 interactors?
How many essential genes in WT are also bem1 synthetic lethals?
What is the dependency of the number of synthetic lethals of specif gene with the fitness of a knockout cell from that gene.
62.3. Method#
I mainly used for this analysis the software Tableau under an academic license, for free.
This software is handy to quickly inspect a difficult dataset with many dimensions and variables.
62.4. Results#
The list of essential genes I downloaded from Here. Essentially it consists of 1110 genes , around 20% of yeast genome , measured in rich media for Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
The reference of the study is [this paper from 2002](Giaever G, et al (2002). Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature, 418:387-91.), called: Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome.
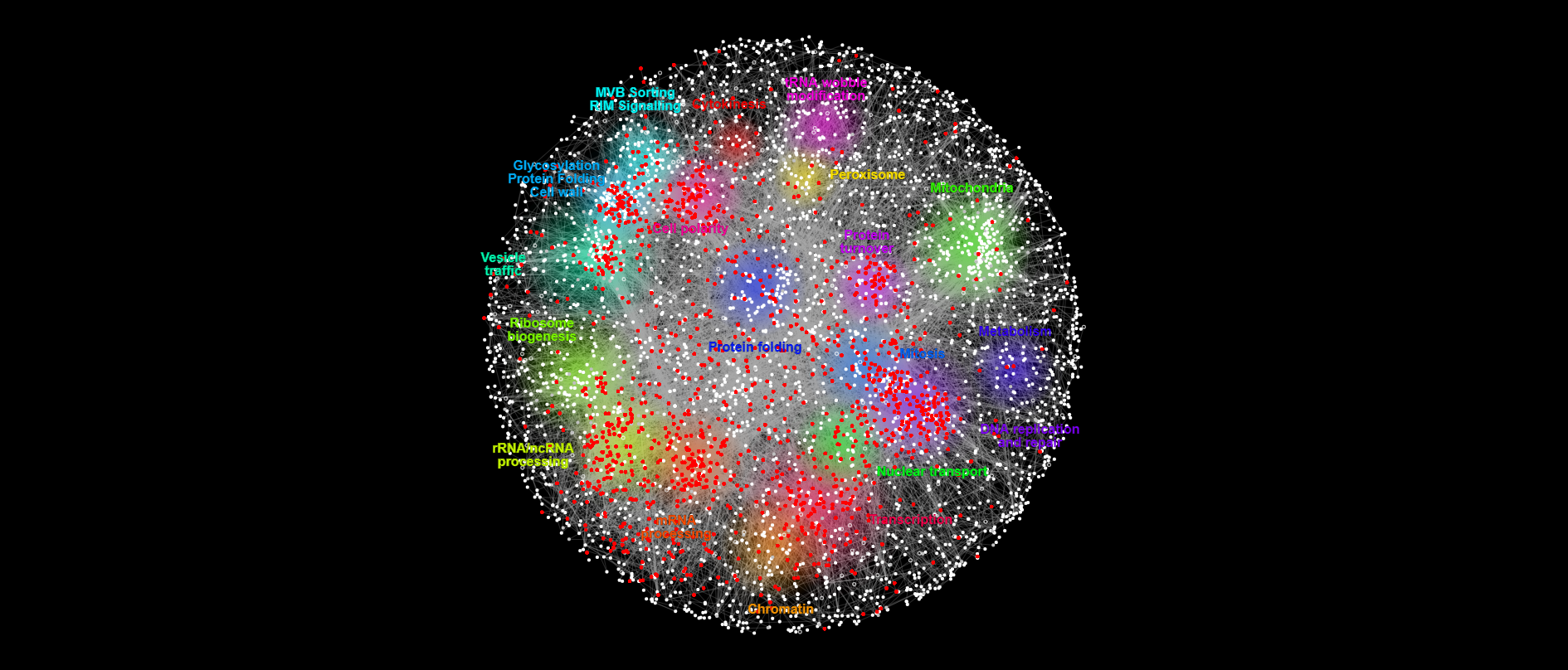 {#fig:essential }
{#fig:essential }How many essential genes in WT are also bem1 interactors?
34 genes out of 321 bem1 interactors genes are also essential in WT. This represents the 3% of all essential genes in WT interacts with Bem1.
Bem1 synthetic lethals mapping -38 genes
 {#fig:lethals}
{#fig:lethals}
How many bem1 synthetic lethals are also essential genes in WT?
Insight 1: Out of the 34 essential genes that intersect with Bem1 interactors, 13 are Bem1 synthetic lethals (~ 1/3 of them ). This means that at least 21 essential genes in WT looses their essentiality in dbem1 background.
Insight 2: 13 genes out of 38 bem1 synthetic lethals are also WT essential genes (~ 1/3 of them). This means that 25 synthetic lethals genes of bem1 have gained essentiality in this background.
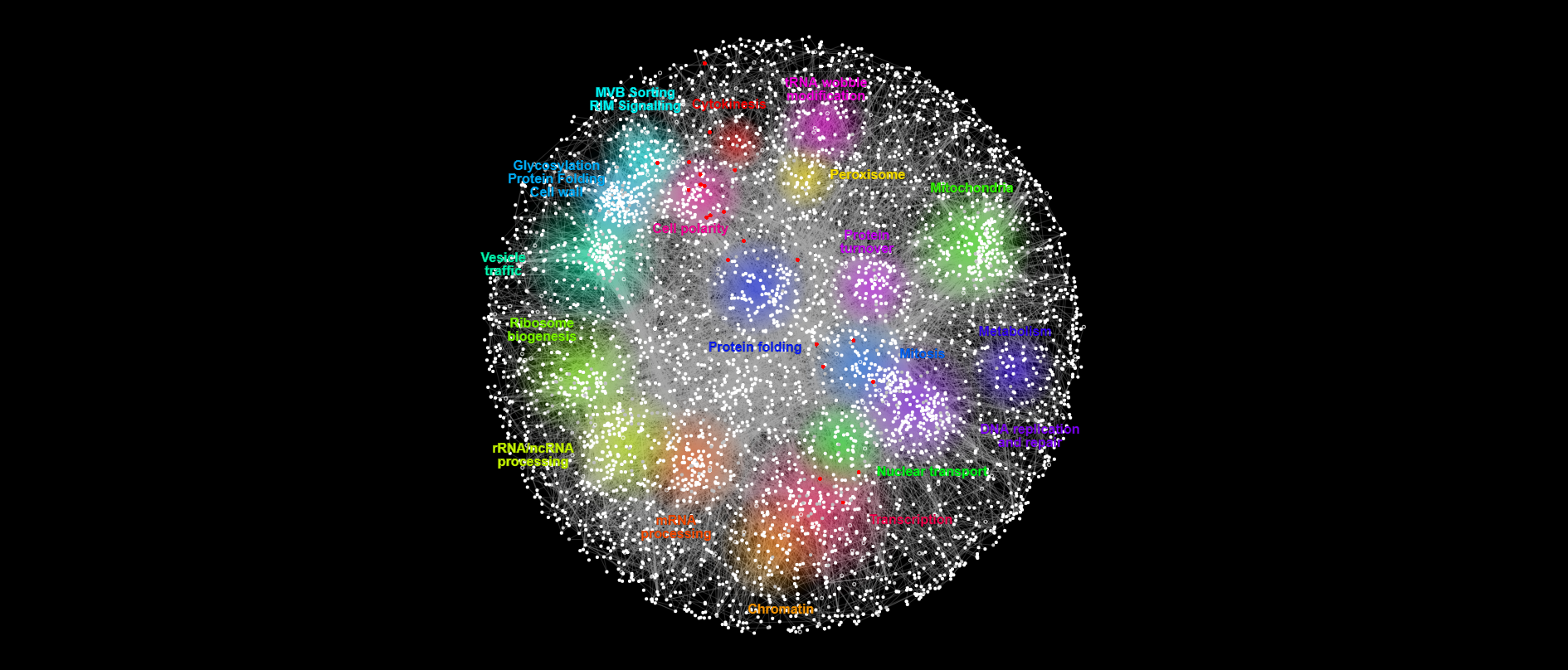 {#fig:intersection-with-Bem1-lethals}
{#fig:intersection-with-Bem1-lethals}
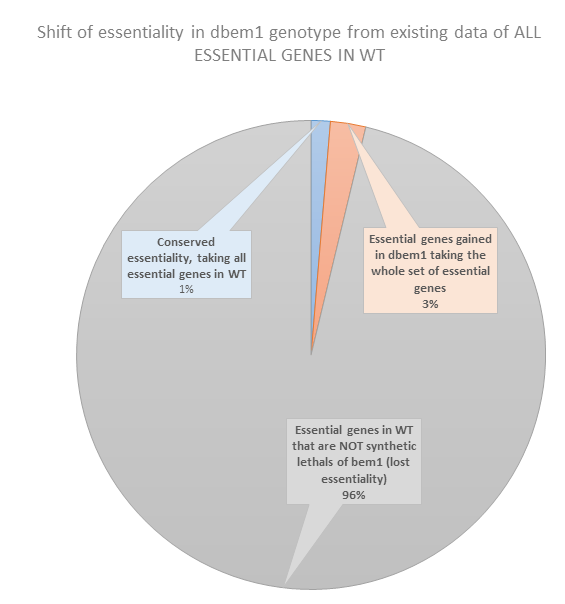
62.5. Conclusion#
Most of the genes that are essential in WT are not synthetic lethals of Bem1.
Is this because they can not be included in the SGA assay? hence they could never pop up because they were never measured…
Following this logic , how can we explained the ones are conserved? this 1% of genes, which includes: cdc42, cdc24 and cdc28.
62.6. Notes#
It is important to note that the synthetic lethals were measured with a subset of nonessential genes from WT.
From ” A. Baryshnikova et al., “Chapter 7 - Synthetic Genetic Array (SGA) Analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe.”” :
This chapter focuses on the application ofSGA analysis to generate double mutant strains and identify genetic interactions among nonessential deletion mutants.
However, SGA can also be applied to examine synthetic genetic interactions involving essential genes. For example, an SGA query strain can be crossed to the Tet-promoter collection (yTHC, Open Biosystems), double mutants can be selected and scored for growth defects in the presence of doxycycline, which downregulates the expression ofthe essential genes (Davierwala et al., 2005). Other essential gene mutant collections (Ben-Aroya et al., 2008; Schuldiner et al., 2005) are now available in arrayed formats and are amenable to genetic interaction analyses using SGA technology (Costanzo et al., in press).
